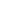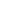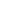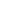LOT 4 Phoenician(?) bronze plate inscriptions & images 1500 BC
Viewed 357 Frequency
Pre-bid 0 Frequency
 Collect
Collect
Name
Size
Description
Translation provided by Youdao
Phoenician (?) bronze plate with images of people, animals and inscriptions on both sides We have done a lot of research on archaic languages. We suggest that the inscriptions are made in old Phoenician language. Opinion of the experts will be highly appreciated. If it is so, this item has a high historical value, because Phoenician alphabet was the first in the history of Europe and Middle East and gave rise to alphabets of many European languages. Provenance: from the old collection of American gentleman, originally purchased in Mediterranean area. Condition: Authentic patina, one side of the plate with several letters inscription is separated. Size: 25.5 cm x 13.5 cm = 10.5" inches x 5.5" inches; Weight: 350 g = 13 oz. Phoenicia was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550 BC to 300 BC. The Phoenicians used the galley, a man-powered sailing vessel, and are credited with the invention of the Bireme. They were famed in Classical Greece and Rome as 'traders in purple', referring to their monopoly on the precious purple dye of the Murex snail, used, among other things, for royal clothing, and for their spread of the alphabet (or abjad), upon which all major modern alphabets are derived. In the Amarna tablets of the 14th century BC, people from the region called themselves Kenaani or Kinaani (Canaanites), although these letters predate the invasion of the Sea Peoples by over a century. Much later, in the 6th century BC, Hecataeus of Miletus writes that Phoenicia was formerly called a name Philo of Byblos later adopted into his mythology as his eponym for the Phoenicians: "Khna who was afterwards called Phoinix". Egyptian seafaring expeditions had already been made to Byblos to bring back "cedars of Lebanon" as early as the third millennium BC. "Phoenicia" is really a Classical Greek term used to refer to the region of the major Canaanite port towns, and does not correspond exactly to a cultural identity that would have been recognized by the Phoenicians themselves. It is uncertain to what extent the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single ethnicity. Their civilization was organized in city-states, similar to ancient Greece. However, in terms of archaeology, language, life style and religion, there is little to set the Phoenicians apart as markedly different from other cultures of Canaan. As Canaanites, they were unique in their remarkable seafaring achievements. Each of their cities was a city-state which was politically an independent unit and they could come into conflict and one city could be dominated by another city-state, although they would collaborate in leagues or alliances. Though ancient boundaries of such city-centered cultures fluctuated, the city of Tyre seems to have been the southernmost. Sarepta (modern day Sarafand) between Sidon and Tyre is the most thoroughly excavated city of the Phoenician homeland. The Phoenicians were the first state-level society to make extensive use of the alphabet. The Phoenician phonetic alphabet is generally believed to be the ancestor of almost all modern alphabets, although it did not contain any vowels (these were added later by the Greeks). From a traditional linguistic perspective, they spoke Phoenician, a Canaanite dialect. However, due to the very slight differences in language, and the insufficient records of the time, whether Phoenician formed a separate and united dialect, or was merely a superficially defined part of a broader language continuum, is unclear. Through their maritime trade, the Phoenicians spread the use of the alphabet to North Africa and Europe, where it was adopted by the Greeks, who later passed it on to the Etruscans, who in turn transmitted it to the Romans. In addition to their many inscriptions, the Phoenicians were believed to have left numerous other types of written sources, but most have not survived. Evangelical Preparation by Eusebius of Caesarea quotes extensively from Philo of Byblos and Sanchuniathon.
Condition Authentic patina, one side of the plate with several letters inscription is separated.
Low Estimate: 20000;
High Estimate: 100000;
Original: Yes;
Circa: 1500 BC
Preview:
Address:
Tampa, FL 33617
Start time:

Online payment is available,
You will be qualified after paid the deposit!

Online payment is available for this session.

Bidding for buyers is available,
please call us for further information. Our hot line is400-010-3636 !

This session is a live auction,
available for online bidding and reserved bidding